What is a Patent?
A patent provides an individual or a business with rights to protect their invention from illegal importing, producing or selling of the product without the permission of the patent holder. To protect their innovative ideas from being taken advantage of, inventors often choose to file for a patent. Filing a patent in India is a legally complex process and it is time consuming. Fortunately, Srisattva offers a hassle-free solution for patent registration, allowing inventors to complete their registration quickly and efficiently.
Patent in India
The Patents Act, 1970, which was amended in 2005 to conform to worldwide norms, regulates the patent status in India. According to the Act, patents are given for brand-new innovations that are inventive, non-obvious, and applicable to industry. There are several stages in the Indian patent application procedure, including filing the application, having it examined, and having it published. After review, a claim may be approved or rejected. Once issued, a patent gives its proprietor the sole authority to make, market, and use the creation for a predetermined amount of time.
What Is Patent Registration?
Patent registration in India is legally demanding. It includes securing exclusive rights to an invention by its creator or owner. It is granted by the government for a specific duration, generally for 20 years, to prevent others from making, using, or selling the invention without the patent owner’s permission. In return, the patent owner must disclose all details and specifications of the invention to the public for further research and development. Srisattva can complete the patent filing online with expert support.
What Can Be Patented in India?
Registration of Patent in India allows inventions related to products, processes, and methods to be patented. This includes but is not limited to chemicals, drugs, pharmaceuticals, software and other latest improvements to the existing innovations. However, the invention must be novel, non-obvious, and have industrial applicability.
What Kind of Inventions Cannot be Patented?
Patent registration in India does not allow the following inventions to be patented:
- The discovery of a natural law or scientific principle
- Literary, theatrical, musical, or artistic works are examples of aesthetic creations
- Plans, guidelines, or techniques for engaging in mental activity, playing games, or conducting business Inventions that violate morality or public order
- Inventions that might be harmful to the environment, animals, or people.
Importance of Patent Registration
Registration of patent in India provides several benefits, including:
- Exclusive rights to the inventor or owner for the invention
- The capacity to prevent unauthorised production, use, or sale of the invention
- The capacity to sell, license, or otherwise dispose of the patent
- The capacity to pursue compensation and legal action against patent infringers
- Encourages research and development and innovation, both of which can stimulate economic growth.
Eligibility Criteria for Patent Register
For completing the patent registration process following eligibility criteria has to be fulfilled in order to file for a registration of patent in India
 |
- Be the inventor or owner of the invention
- The invention must be new
- The invention should not be published in the public
- The applicant must provide a detailed description and specifications of the invention.
Documents for Filing Patent Registration Application
The following documents are to be submitted along with a patent registration application:
- A complete specification of the invention, including the details of how it works and its applications
- A provisional application for the patent
- A declaration of inventorship and ownership of the invention
- Drawings and diagrams of the invention, if applicable
- Details of the applicant or owner of the invention.
Forms Required to be Filed for Patent Registration Application
For the registration of patent in India the following forms must be submitted to the Indian patent office:
- Form 1: This is the application form for the grant of a patent and includes details of the applicant, the invention, and its claims
- Form 2: This form is used to furnish the details of the priority application filed by the applicant, if any
- Form 3: This form is used to furnish the details of the inventors of the patent
- Form 5: It is used to furnish the details of the government undertaking, if any, to which the patent is to be assigned
- Form 26: This form is used to furnish the details of the exclusive marketing rights, if any, claimed by the applicant.
Where to File a Patent Application?
It’s filed at the appropriate patent office using Form-1 and a provisional/complete specification, along with the required fee. The following factors are used to determine a patent office’s jurisdiction –
- The jurisdiction of the patent office is determined by the applicant’s place of residence, domicile, or business, with the first mentioned applicant’s place considered in the case of joint applicants
- The origin of the invention also plays a role in determining the patent office’s jurisdiction
- If the applicant is a foreign entity without a business or domicile in India, the designated address for service in India is taken into consideration
- Considering these factors is crucial for accurate and efficient processing of patent registration in India.
Mumbai Patent Office Jurisdiction
- The Mumbai Patent Office is responsible for patent-related matters in multiple territories
- These territories include the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Goa
- The Mumbai Patent Office is also responsible for patent-related matters in the Union Territories of Daman & Diu, and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
Delhi Patent Office Jurisdiction
- The Delhi Patent Office has jurisdiction over several states and territories in India
- These include Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and the national capital territory of Delhi
- The Delhi patent office is also responsible for patent-related matters in the Union Territory of chandigarh.
Chennai Patent Office Jurisdiction
- The Chennai Patent Office is responsible for managing patent-related affairs in multiple regions
- These regions include the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu
- The Chennai Patent Office is also responsible for patent-related matters in the Union Territories of Pondicherry and Lakshadweep.
Kolkata Patent Office Jurisdiction
- The Kolkata Patent Office has jurisdiction over several territories in India
- These territories include the states of Bihar, Orissa, West Bengal, Sikkim, Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur, Tripura, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh
- The Kolkata Patent Office is also responsible for patent-related matters in the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, covering a significant portion of India.
Trademark vs Copyright vs Patent
|
Trademark |
Patent |
Copyright |
|
|
What’s Protected |
Anything that identifies and distinguishes the source of one party’s commodities from those of another party, whether it be a word, phrase, symbol, or design. |
Inventions, including procedural, manufacturing, compositional, and material machines, as well as upgrades to these. |
Among other creative works of authorship, there are books, articles, songs, photographs, sculptures, dances, sound recordings, and motion pictures. |
|
Requirements for Protection |
A mark needs to be recognisable in the sense that it needs to be able to pinpoint the origin of a particular good. |
It calls for a brand-new, worthwhile, and interesting invention. |
A work ought to be distinctive, creative, and physically generated. |
|
Term of Protection |
Whenever the trademark is used commercially. | 20 years | Author’s lifespan span+ 70 years. |
|
Rights Granted |
Right to make use of the mark and to forbid third parties from making use of the same mark in a manner that might lead to confusion regarding the source of the products or services. |
Right to prevent the patented invention from being manufactured, sold, or imported by others. | Copyrighted works have the authority to restrict their use, distribution, performance in public, and display. |
Drafting of patent application
The drafting of a patent application is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of patent law and a thorough understanding of the invention. The patent application must be drafted in a clear and concise manner, and it must meet all of the requirements of the Indian Patent Act, 1970.
The following are some of the key elements of a patent application:
- Title: The title of the patent application should be clear and concise, and it should accurately describe the invention.
- Abstract: The abstract is a brief summary of the invention. It should be no more than 150 words, and it should be written in a clear and concise manner.
- Description: The description is a detailed explanation of the invention. It should include all of the information that is necessary for someone to understand and implement the invention.
- Claims: The claims define the scope of the invention. They should be clear and concise, and they should be supported by the description.
Rules to keep in mind while filing the patent application
The following are some of the rules to keep in mind while filing the patent application:
- The patent application must be filed with the Indian Patent Office.
- The patent application must be filed in the name of the inventor(s).
- The patent application must be complete and accurate.
- The patent application must be accompanied by the prescribed fees.
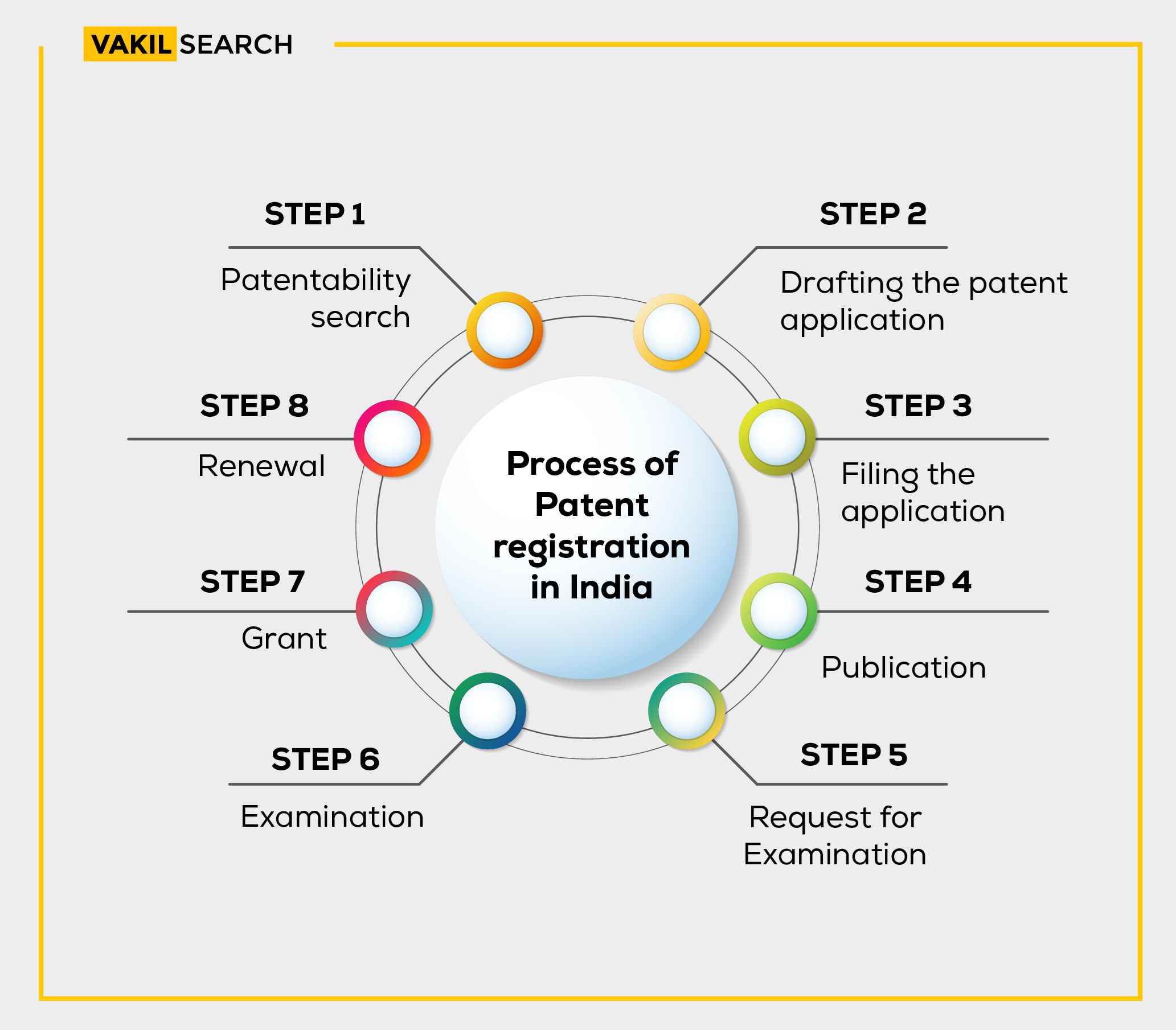
Steps: Patent Registration Process
The process of patent registration in India involves the following steps:
- Step 1: File the patent registration application with all the needed documents
- Step 2: After the application is filed, it is published in the official journal, which is available to the public
- Step 3: Submit a request for the patent application’s evaluation. The patent office will review the application after receiving the request for examination and issue a report on the invention’s patentability
- Step 4: If the patent office is satisfied with the patentability of the invention, it will grant the patent to the applicant.
Will Patent Registration in India Protect My Invention Outside India as Well?
A patent that has been registered in India is only valid there, and its owner is not permitted to use its rights outside of India. However, if the patent holder desires patent protection in additional countries, they must submit an application within 12 months following the patent’s registration in India.
Types of Patent Application in India
In India, the following types of patent applications can be filed for patent registration process
- Ordinary Application: This is the most common type of application and is filed by the applicant directly with the patent office
- Convention Application: It is filed by an applicant who has already filed a patent application in a convention country
- PCT International Application: This application is filed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) and is recognised in all member countries.
Validity Period of the Registered Patent Registration:
The validity period of a registered patent is 20 years from the date of filing
What Is Patent Renewal?
Patent renewal is the process of extending the validity of a patent by paying the prescribed renewal fee. The renewal fee must be paid before the expiration
Can a Patent be Revoked in India?
Yes, one can be revoked in India under the following circumstances, such as:
- Non-payment of renewal fees
- Non-working of the patented invention
- Public interest
What Is Patent Assignment?
Patent assignment is the process of transferring ownership of a patent from the original owner to a new owner through a patent assignment agreement.
Facts About Patent Filing in India
- The first-to-file method is used in India to register patents
- There are four offices of the Indian patent office, and they are in Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, and Chennai
- Patent applications in India can be filed in English or Hindi
- In India, the patentability of an invention is determined based on the novelty, inventive step, and industrial applicability of the invention.
Non Patentable Inventions in India
As per the Indian Patent Act, Sections 3 and 4, the following inventions are not considered patentable in India:
- An invention that is considered frivolous or trivial
- An invention that claims anything which is obviously against well-established natural laws
- The mere discovery of a scientific principle
- An invention whose primary intention or use is against the law or morality, or which can cause harm to public health
- The formulation of an abstract theory
- The mere discovery of a new form of a known invention, which does not lead to an improvement in the known effectiveness of that particular invention
- The mere discovery of any new property or new use for a known substance, or the mere use of a known process, machine, or apparatus, unless it results in a new product or uses at least one new reactant
- A device obtained by a mere admixture that only results in the combination of the properties of its components or a process to produce such substance
- The mere arrangement or duplication or rearrangement of known devices, each functioning independently in a known way
- A method of agriculture or horticulture.
Patent Registration Cost in India
The formal patent fee for submitting a patent application is ₹1,600 for an individual or ₹4000 for a small or ₹8000 large entity. The cost of an attorney to prepare a provisional patent filing can be between ₹20,000 and ₹35,000. If you intend to sell your concept, procedure, technique, or invention, you should presumably submit an application for protection. The need for protection and the places you will operate in will determine security. So a patent is what we need to safeguard our invention.
What Are the Recent/Last Amendments in the Patent Act, 1970?
The most recent amendments to The Patent Act, 1970 were made in 2019. These amendments introduced several changes, such as:
- Software and business procedures are now included in the definition of an invention that qualifies for patent protection
- The term for the grant of a patent for pharmaceutical products was increased from 20 years to 20 years plus an additional 5 years
- The procedure for the expedited examination of patent applications was introduced.
Why Srisattva?
Srisattva is an excellent choice for businesses and individuals looking to protect their intellectual property through patent registration services. With their experienced and knowledgeable team of patent attorneys, Srisattva provides comprehensive patent registration services that cover all aspects of the process, from conducting patent searches to filing the patent application and obtaining the patent registration certificate. Our user-friendly online platform makes it easy for you to track the status of their patent application, and their competitive pricing and transparent fee structure ensure that clients get the best value for their money. Overall, Srisattva’s patent registration services are an excellent investment for any business or individual looking to protect their innovative ideas and inventions.
Recent Updates
For the first time in 11 years the total number of domestic patent filings have surpassed overseas filing in India. Information was confirmed by Prime minister Narendra Modi directly on the monthly radio address Mann-Ki-baat. The Indian institute of science Bangalore in itself has made and registered 145 patents. These numbers clearly showcase and increase the drive towards innovation in India.






